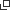Report 10-Healthcare Habits of Women in Indonesia

Overview
- Indonesia has the second-highest number of locally operating Japanese companies after China.
- Women’s participation in society is high.
- Many women purchase OTC drugs and supplements at personal care stores/drug stores.
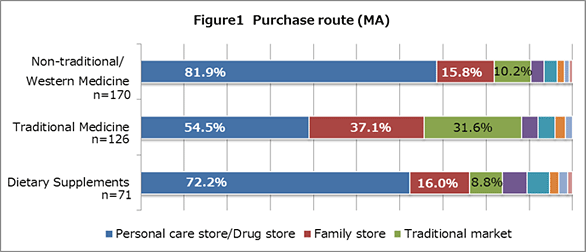
- They get information on healthcare products mostly from TV.
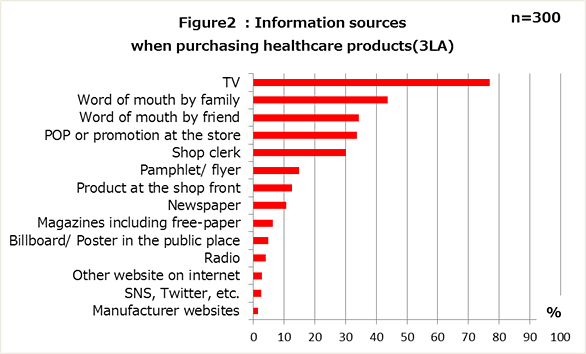
- Some 40% of women "want to purchase Japanese-made healthcare products".
Analysis
Indonesia: A Major ASEAN Player
The Republic of Indonesia has more than five times the land area of Japan and the fourth largest population in the world (approx. 247 million)(*1). Currently, some 1,255 Japanese companies(*2) operate in Indonesia—the second-highest number after China(*3). Indonesia is a key member of the ASEAN organization, and has been growing rapidly in recent years. 88.1% of its population is Muslim(*1), making it the world’s most populous Islamic nation. When living or doing business in Indonesia, consideration must be given to daily prayer, diet (pork and alcohol are forbidden), Ramadan, and similar cultural factors.
Indonesia is considered to be relatively open and accepting. There is a high rate of female participation in society. By way of example, both the current Minister of Tourism and Creative Economy and the Minister of the National Development Planning Agency are women. Moreover, some 51% of women in the country work (as opposed to 48% in Japan)(*4). Even the Hijabs used to cover a woman’s hair in Indonesia are sold in various vibrant colors and designs. There are also a number of increasingly popular websites specifically dedicated to Muslim fashion. Amid these trends, more attention is being paid not only to the social position of women in Indonesia, but also to their purchasing power.

Indonesian women(*5)
Healthcare products are purchased at personal care stores/drug stores after seeing on TV. Japanese products continue to be popular.
In Jakarta, face-to-face interviews were conducted with 300 randomly sampled women between the ages of 20 and 59. The women were asked about their values, customs and habits, as well as what products they buy and where they buy them. This article focuses on their purchasing of OTC drugs and supplements, and on their interest in Japan.
Whether buying Western medicine, traditional medicine, or supplements, the majority of respondents said that they make most of their purchases at personal care stores/drug stores. Regardless of the type of product, convenience stores, supermarkets, the Internet, hypermarkets, and department stores followed from fourth place on (see Figure 1). Moreover, close to 80% of respondents got their information on healthcare products from TV. The Internet did not even place in the top five (see Figure 2).
In regard to affinity with Japan, which may be of particular interest to Japanese readers, respondents were asked to select from 18 different countries offered as response options. 40.0% answered that they "want to buy Japanese-made healthcare products".
- *1 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan
- *2 JETRO
- *3 "Kaigai Shinshitsu Kigyo Soran (Directory of Japanese Companies with Overseas Operations)," Toyo Keizai, Inc.
- *4 World Bank
- *5 Youharman (author)
Survey Overview
| Survey Method | Interviews conducted annually by INTAGE. Research on purchase behavior, values, preferences, etc. conducted among 300 women aged 20-59, 1,500 in total, living in Ho Chi Minh City, Bangkok, Jakarta, Shanghai, and Delhi. |
|---|---|
| Organization Conducting the Survey | INTAGE Inc. |
ASIA INSIGHT REPORT
INTAGE Inc. publishes the "Asia Insight Report" based on independent surveys conducted in the Asian region in collaboration with overseas INTAGE subsidiaries to identify trends in attitudes and behavior on a variety of themes.